Dynamic Devices
Each sub-type is composed of the corresponding dynamic components that define the model. As a result, it is possible to flexibly define dynamic data models and methods according to the analysis requirements. DynamicInjection components use parametric a parametric type pattern to materialize the full specification of the dynamic injection model with parameters. This design enable the use of parametric methods to specify the mathematical model of the dynamic components separately.
DynamicInjection components also implement some additional information useful for the modeling like the usual states assumed by the model and the number. These values are derived from the documentation associated with the model, for instance PSS/e models provide parameters, states and variables. Although PowerSystems.jl doesn't assume a specific mathematical model for the components, the default values for these parameters are derived directly from the data model source.
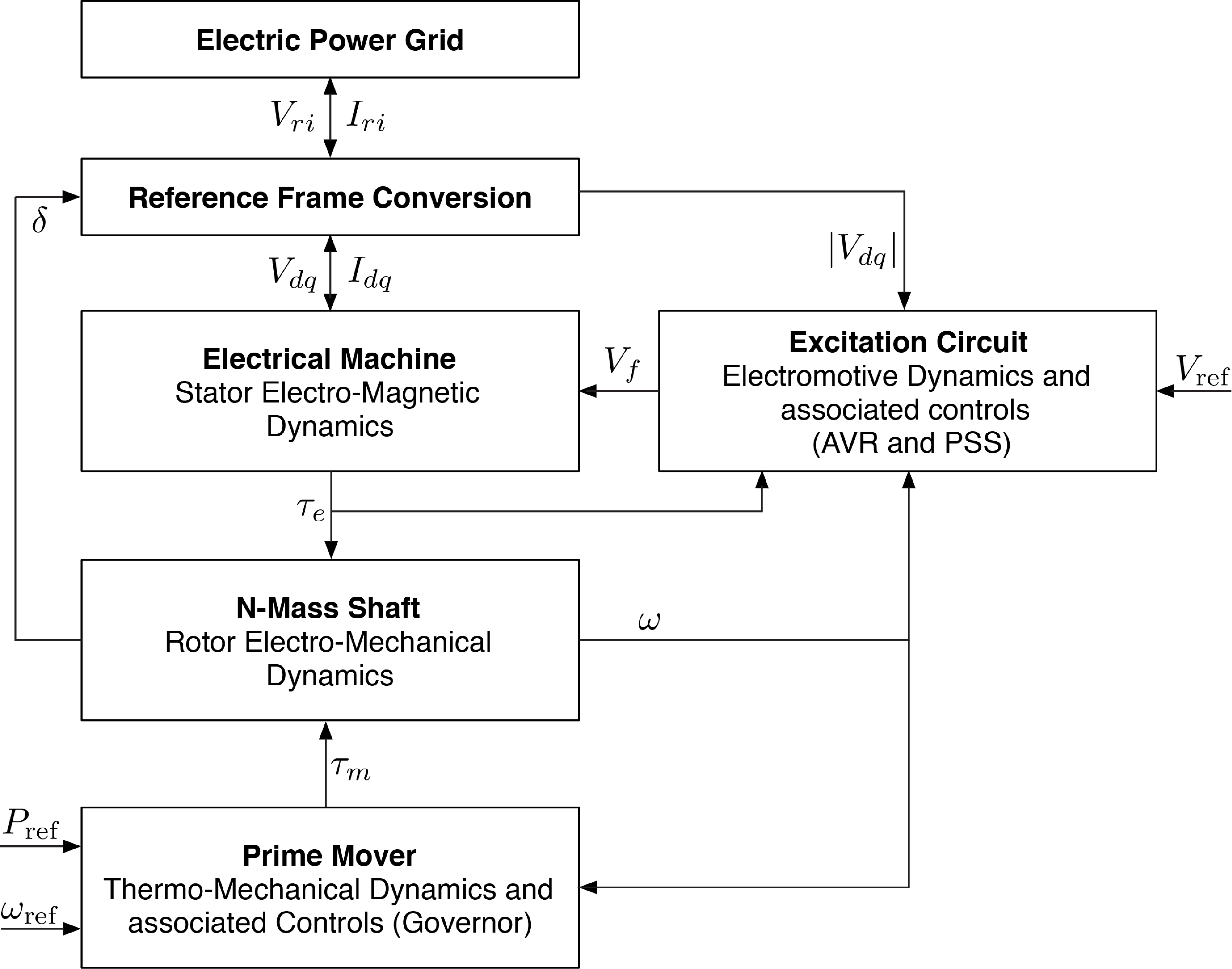
Dynamic Generator
Each generator is a data structure that is defined by the following components:
- Machine: That defines the stator electro-magnetic dynamics.
- Shaft: That describes the rotor electro-mechanical dynamics.
- Automatic Voltage Regulator: Electromotive dynamics to model an AVR controller.
- Power System Stabilizer: Control dynamics to define an stabilization signal for the AVR.
- Prime Mover and Turbine Governor: Thermo-mechanical dynamics and associated controllers.
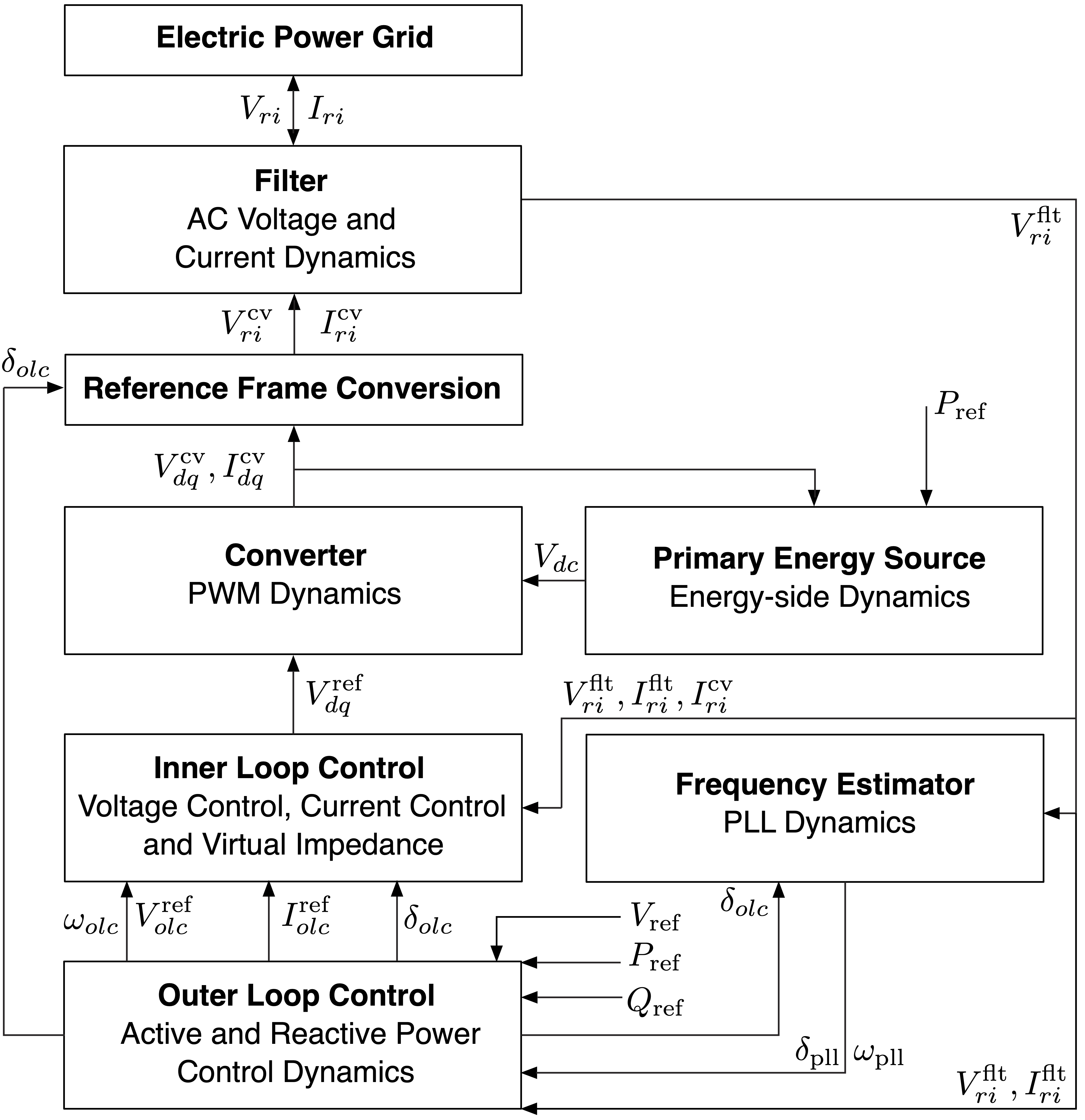
Each inverter is a data structure that is defined by the following components:
- DC Source: Defines the dynamics of the DC side of the converter.
- Frequency Estimator: That describes how the frequency of the grid can be estimated using the grid voltages. Typically a phase-locked loop (PLL).
- Outer Loop Control: That describes the active and reactive power control dynamics.
- Inner Loop Control: That can describe virtual impedance, voltage control and current control dynamics.
- Converter: That describes the dynamics of the pulse width modulation (PWM) or space vector modulation (SVM).
- Filter: Used to connect the converter output to the grid.
⠀